We are makers. We humans love to create and invent. Some of our inventions are hideous, laughable or just plain evil — Twinkies, collateralized debt obligations and subprime mortgages, Agent Orange, hair extensions, spray-on tans, cluster bombs, diet water.
However, for every misguided invention comes something truly great. This time, a prosthetic hand that provides a sense of real feeling, courtesy of the makers of the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Cleveland, Ohio.
From Technology Review:
Igor Spetic’s hand was in a fist when it was severed by a forging hammer three years ago as he made an aluminum jet part at his job. For months afterward, he felt a phantom limb still clenched and throbbing with pain. “Some days it felt just like it did when it got injured,” he recalls.
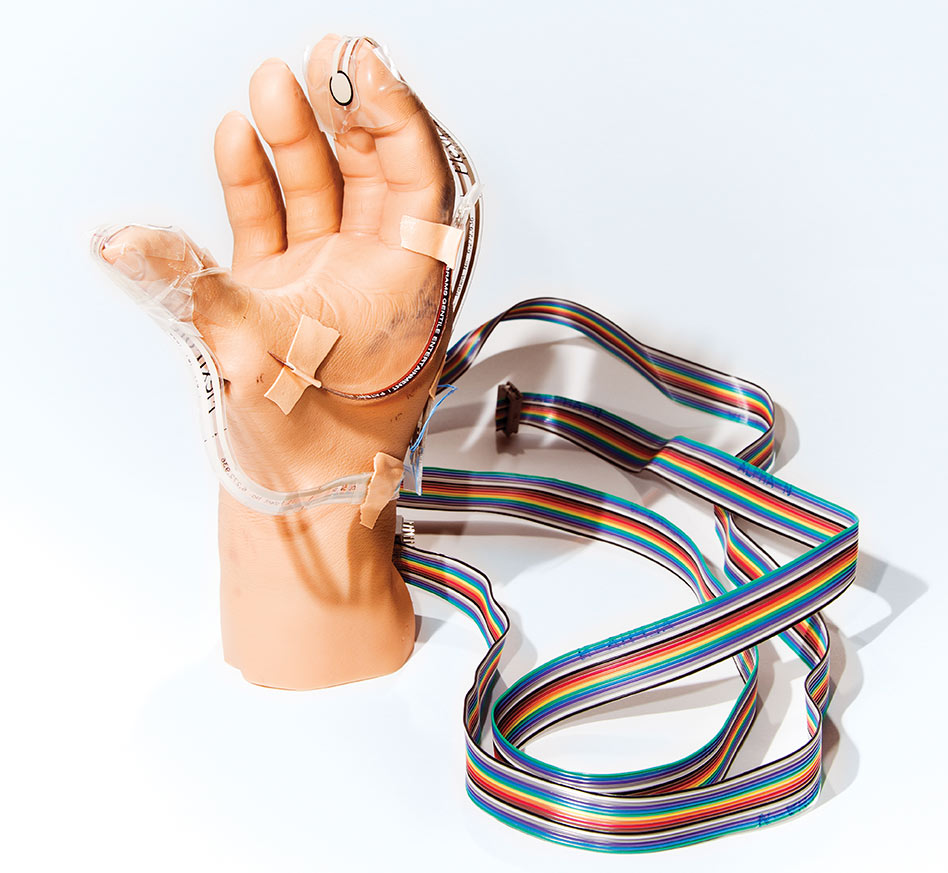
He soon got a prosthesis. But for amputees like Spetic, these are more tools than limbs. Because the prosthetics can’t convey sensations, people wearing them can’t feel when they have dropped or crushed something.Now Spetic, 48, is getting some of his sensation back through electrodes that have been wired to residual nerves in his arm. Spetic is one of two people in an early trial that takes him from his home in Madison, Ohio, to the Cleveland Veterans Affairs Medical Center. In a basement lab, his prosthetic hand is rigged with force sensors that are plugged into 20 wires protruding from his upper right arm. These lead to three surgically implanted interfaces, seven millimeters long, with as many as eight electrodes apiece encased in a polymer, that surround three major nerves in Spetic’s forearm.
On a table, a nondescript white box of custom electronics does a crucial job: translating information from the sensors on Spetic’s prosthesis into a series of electrical pulses that the interfaces can translate into sensations. This technology “is 20 years in the making,” says the trial’s leader, Dustin Tyler, a professor of biomedical engineering at Case Western Reserve University and an expert in neural interfaces.
As of February, the implants had been in place and performing well in tests for more than a year and a half. Tyler’s group, drawing on years of neuroscience research on the signaling mechanisms that underlie sensation, has developed a library of patterns of electrical pulses to send to the arm nerves, varied in strength and timing. Spetic says that these different stimulus patterns produce distinct and realistic feelings in 20 spots on his prosthetic hand and fingers. The sensations include pressing on a ball bearing, pressing on the tip of a pen, brushing against a cotton ball, and touching sandpaper, he says. A surprising side effect: on the first day of tests, Spetic says, his phantom fist felt open, and after several months the phantom pain was “95 percent gone.”
On this day, Spetic faces a simple challenge: seeing whether he can feel a foam block. He dons a blindfold and noise-canceling headphones (to make sure he’s relying only on his sense of touch), and then a postdoc holds the block inside his wide-open prosthetic hand and taps him on the shoulder. Spetic closes his prosthesis—a task made possible by existing commercial interfaces to residual arm muscles—and reports the moment he touches the block: success.
Read the entire article here.
Image: Prosthetic hand. Courtesy of MIT Technology Review / Veterans Affairs Medical Center.