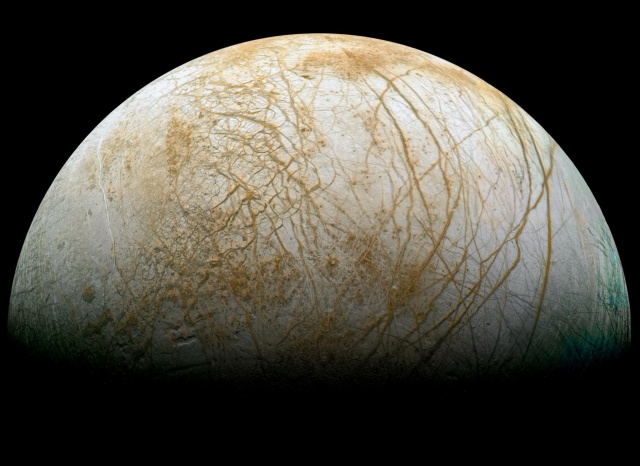
With the the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Philae lander firmly rooted to a comet, NASA’s Dawn probe orbiting dwarf planet Ceres and its New Horizon’s spacecraft hurtling towards Pluto and Charon it would seem that we are doing lots of extraterrestrial exploration lately. Well, this is exciting, but for arm-chair explorers like myself this is still not enough. So, three cheers to NASA for giving a recent thumbs up to their next great mission — Europa Multi Flyby — to Jupiter’s moon, Europa.
Development is a go! But we’ll have to wait until the mid-2020s for lift-off. And, better yet, ESA has a mission to Europa planned for launch in 2022. Can’t wait — it looks spectacular.
From ars technica:
Get ready, we’re going to Europa! NASA’s plan to send a spacecraft to explore Jupiter’s moon just passed a major hurdle. The mission, planned for the 2020s, now has NASA’s official stamp of approval and was given the green light to move from concept phase to development phase.
Formerly known as Europa Clipper, the mission will temporarily be referred to as the Europa Multi Flyby Mission until it is given an official name. The current mission plan would include 45 separate flybys around the moon while orbiting Jupiter every two weeks. “We are taking an exciting step from concept to mission in our quest to find signs of life beyond Earth,” John Grunsfeld, associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, said in a press release.
Since Galileo first turned a spyglass up to the skies and discovered the Jovian moon, Europa has been a world of intrigue. In the 1970s, we received our first look at Europa through the eyes of Pioneer 10 and 11, followed closely by the twin Voyager satellites in the 1980s. Their images provided the first detailed view of the Solar System’s smoothest body. These photos also delivered evidence that the moon might be harboring a subsurface ocean. In the mid 1990s, the Galileo spacecraft gave us the best view to-date of Europa’s surface.
“Observations of Europa have provided us with tantalizing clues over the last two decades, and the time has come to seek answers to one of humanity’s most profound questions,” Grunsfeld said. “Mainly, is there life beyond Earth?”
Sending a probe to explore Jupiter’s icy companion will help scientists in the search for this life. If Europa can support microbial life, other glacial moons such as Enceladus might as well.
Water, chemistry, and energy are three components essential to the presence of life. Liquid water is present throughout the Solar System, but so far the only world known to support life is Earth. Scientists think that if we follow the water, we may find evidence of life beyond Earth.
However, water alone will not support life; the right combination of ingredients is key. This mission to Europa will explore the moon’s potential habitability as opposed to outright looking for life.
When we set out to explore new worlds, we do it in phases. First we flyby, then we send robotic landers, and then we send people. This three-step process is how we, as humans, have explored the Moon and how we are partly through the process of exploring Mars.
The flyby of Europa will be a preliminary mission with four objectives: explore the ice shell and subsurface ocean; determine the composition, distribution, and chemistry of various compounds and how they relate to the ocean composition; map surface features and determine if there is current geologic activity; characterize sites to determine where a future lander might safely touch down.
Europa, at 3,100 kilometers wide (1,900 miles), is the sixth largest moon in the Solar System. It has a 15 to 30 kilometer (9 to 18 mile) thick icy outer crust that covers a salty subsurface ocean. If that ocean is in contact with Europa’s rocky mantle, a number of complex chemical reactions are possible. Scientists think that hydrothermal vents lurk on the seafloor, and, just like the vents here on Earth, they could support life.
The Galileo orbiter taught us most of what we know about Europa through 12 flybys of the icy moon. The new mission is scheduled to conduct approximately 45 flybys over a 2.5-year period, providing even more insight into the moon’s habitability.
Read the article here.
Image: Europa. Europa is Jupiter’s sixth-closest moon, and the sixth-largest moon in the Solar System. Courtesy of NASA.