Last week’s announcement that cosmologists had found signals of gravitational waves from the primordial cosmic microwave background of the Big Bang made many headlines, even on cable news. If verified by separate experiments this will be ground-breaking news indeed — much like the discovery of the Higgs Boson in 2012. Should the result stand, this may well pave the way for new physics and greater support for the multiverse theory of the universe. So, in addition to the notion that we may not be alone in the vast cosmos, we’ll now have to consider not being alone in a cosmos made up of multiple universes — our universe may not be alone either!
From the New Scientist:
Wave hello to the multiverse? Ripples in the very fabric of the cosmos, unveiled this week, are allowing us to peer further back in time than anyone thought possible, showing us what was happening in the first slivers of a second after the big bang.
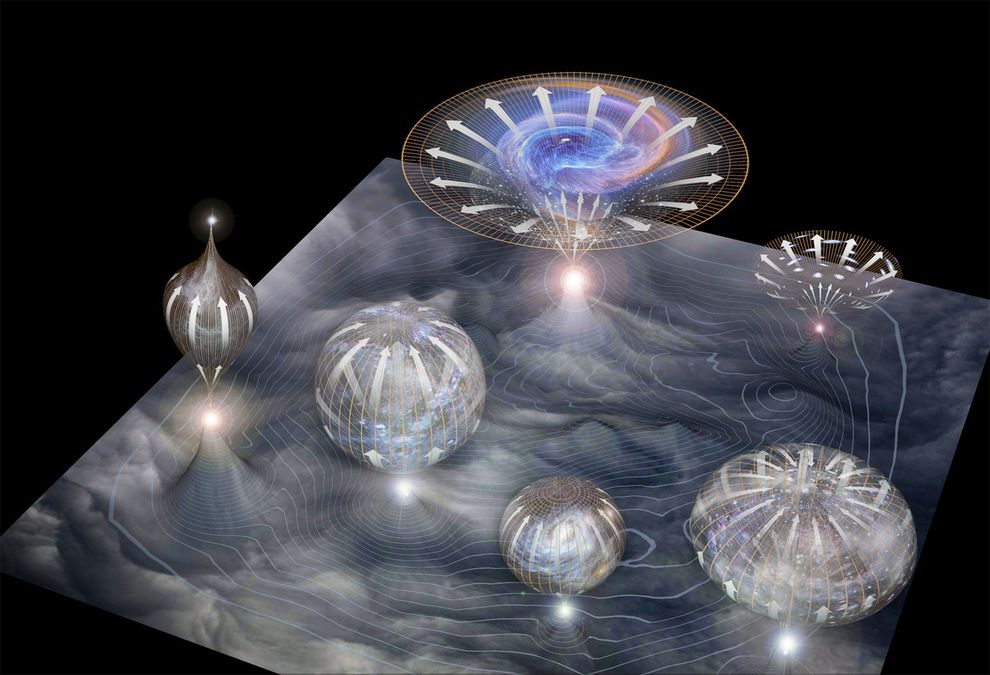
The discovery of these primordial waves could solidify the idea that our young universe went through a rapid growth spurt called inflation. And that theory is linked to the idea that the universe is constantly giving birth to smaller “pocket” universes within an ever-expanding multiverse.
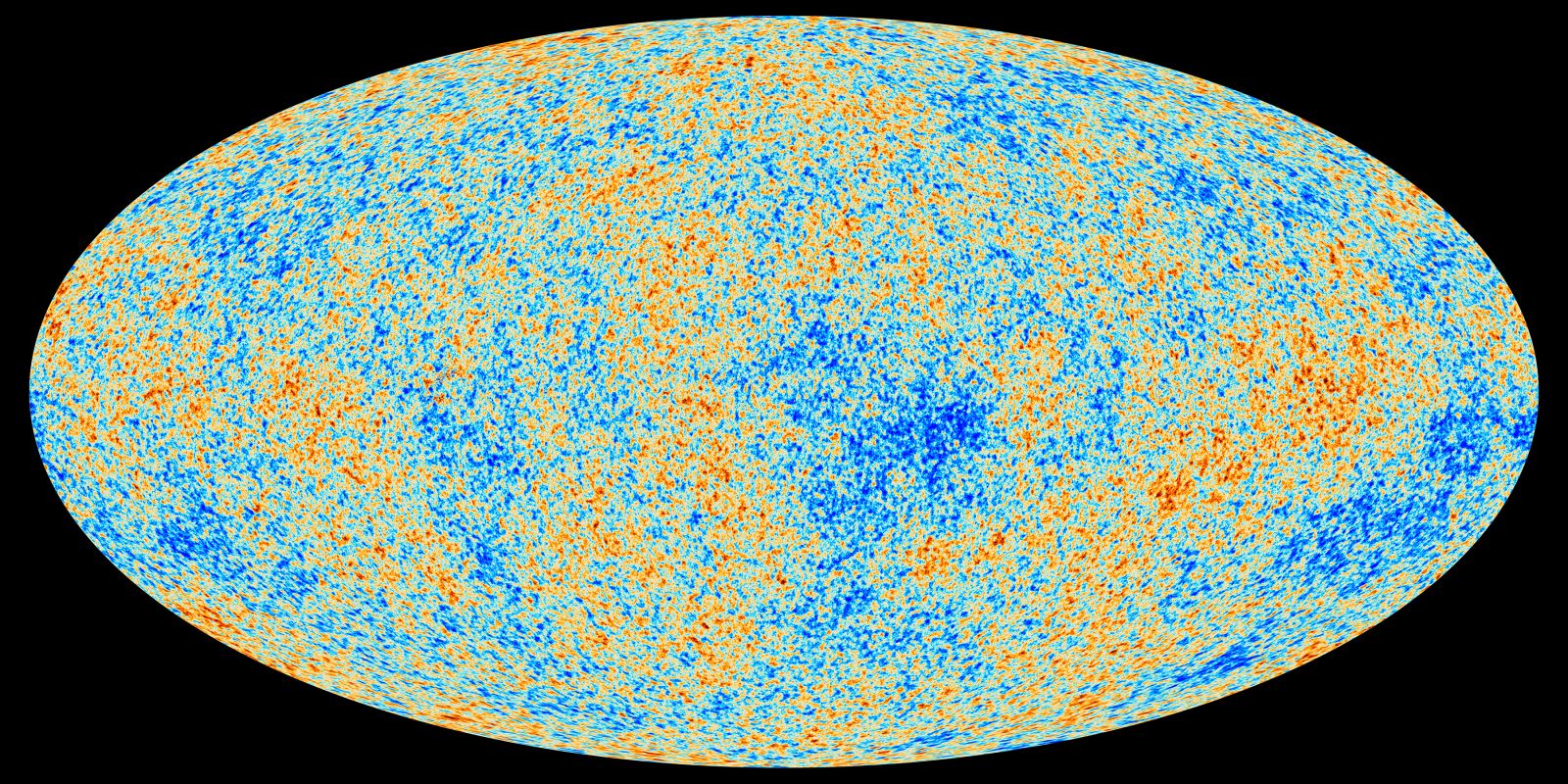
The waves in question are called gravitational waves, and they appear in Einstein’s highly successful theory of general relativity (see “A surfer’s guide to gravitational waves”). On 17 March, scientists working with the BICEP2 telescope in Antarctica announced the first indirect detection of primordial gravitational waves. This version of the ripples was predicted to be visible in maps of the cosmic microwave background (CMB), the earliest light emitted in the universe, roughly 380,000 years after the big bang.
Repulsive gravity
The BICEP2 team had spent three years analysing CMB data, looking for a distinctive curling pattern called B-mode polarisation. These swirls indicate that the light of the CMB has been twisted, or polarised, into specific curling alignments. In two papers published online on the BICEP project website, the team said they have high confidence the B-mode pattern is there, and that they can rule out alternative explanations such as dust in our own galaxy, distortions caused by the gravity of other galaxies and errors introduced by the telescope itself. That suggests the swirls could have been left only by the very first gravitational waves being stretched out by inflation.
“If confirmed, this result would constitute the most important breakthrough in cosmology over the past 15 years. It will open a new window into the beginning of our universe and have fundamental implications for extensions of the standard model of physics,” says Avi Loeb at Harvard University. “If it is real, the signal will likely lead to a Nobel prize.”
And for some theorists, simply proving that inflation happened at all would be a sign of the multiverse.
“If inflation is there, the multiverse is there,” said Andrei Linde of Stanford University in California, who is not on the BICEP2 team and is one of the originators of inflationary theory. “Each observation that brings better credence to inflation brings us closer to establishing that the multiverse is real.” (Watch video of Linde being surprised with the news that primordial gravitational waves have been detected.)
The simplest models of inflation, which the BICEP2 results seem to support, require a particle called an inflaton to push space-time apart at high speed.
“Inflation depends on a kind of material that turns gravity on its head and causes it to be repulsive,” says Alan Guth at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, another author of inflationary theory. Theory says the inflaton particle decays over time like a radioactive element, so for inflation to work, these hypothetical particles would need to last longer than the period of inflation itself. Afterwards, inflatons would continue to drive inflation in whatever pockets of the universe they inhabit, repeatedly blowing new universes into existence that then rapidly inflate before settling down. This “eternal inflation” produces infinite pocket universes to create a multiverse.
Quantum harmony
For now, physicists don’t know how they might observe the multiverse and confirm that it exists. “But when the idea of inflation was proposed 30 years ago, it was a figment of theoretical imagination,” says Marc Kamionkowski at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, Maryland. “What I’m hoping is that with these results, other theorists out there will start to think deeply about the multiverse, so that 20 years from now we can have a press conference saying we’ve found evidence of it.”
In the meantime, studying the properties of the swirls in the CMB might reveal details of what the cosmos was like just after its birth. The power and frequency of the waves seen by BICEP2 show that they were rippling through a particle soup with an energy of about 1016 gigaelectronvolts, or 10 trillion times the peak energy expected at the Large Hadron Collider. At such high energies, physicists expect that three of the four fundamental forces in physics – the strong, weak and electromagnetic forces – would be merged into one.
The detection is also the first whiff of quantum gravity, one of the thorniest puzzles in modern physics. Right now, theories of quantum mechanics can explain the behaviour of elementary particles and those three fundamental forces, but the equations fall apart when the fourth force, gravity, is added to the mix. Seeing gravitational waves in the CMB means that gravity is probably linked to a particle called the graviton, which in turn is governed by quantum mechanics. Finding these primordial waves won’t tell us how quantum mechanics and gravity are unified, says Kamionkowski. “But it does tell us that gravity obeys quantum laws.”
“For the first time, we’re directly testing an aspect of quantum gravity,” says Frank Wilczek at MIT. “We’re seeing gravitons imprinted on the sky.”
Waiting for Planck
Given the huge potential of these results, scientists will be eagerly anticipating polarisation maps from projects such as the POLARBEAR experiment in Chile or the South Pole Telescope. The next full-sky CMB maps from the Planck space telescope are also expected to include polarisation data. Seeing a similar signal from one or more of these experiments would shore up the BICEP2 findings and make a firm case for inflation and boost hints of the multiverse and quantum gravity.
One possible wrinkle is that previous temperature maps of the CMB suggested that the signal from primordial gravitational waves should be much weaker that what BICEP2 is seeing. Those results set theorists bickering about whether inflation really happened and whether it could create a multiverse. Several physicists suggested that we scrap the idea entirely for a new model of cosmic birth.
Taken alone, the BICEP2 results give a strong-enough signal to clinch inflation and put the multiverse back in the game. But the tension with previous maps is worrying, says Paul Steinhardt at Princeton University, who helped to develop the original theory of inflation but has since grown sceptical of it.
“If you look at the best-fit models with the new data added, they’re bizarre,” Steinhardt says. “If it remains like that, it requires adding extra fields, extra parameters, and you get really rather ugly-looking models.”
Forthcoming data from Planck should help resolve the issue, and we may not have long to wait. Olivier Doré at the California Institute of Technology is a member of the Planck collaboration. He says that the BICEP2 results are strong and that his group should soon be adding their data to the inflation debate: “Planck in particular will have something to say about it as soon as we publish our polarisation result in October 2014.”
Read the entire article here.
Image: Multiverse illustration. Courtesy of National Geographic.