 You might expect to find police drones in the pages of a science fiction novel by Philip K. Dick or Iain M. Banks. But by 2015, citizens of the United States may well see these unmanned flying machines patrolling the skies over the homeland. The U.S. government recently pledged to loosen Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) restrictions that would allow local law enforcement agencies to use drones in just a few short years. So, soon the least of your worries will be traffic signal cameras and the local police officer armed with a radar gun. Our home-grown drones are likely to be deployed first for surveillance. But, undoubtedly armaments will follow. Hellfire missiles over Helena, Montana anyone?
You might expect to find police drones in the pages of a science fiction novel by Philip K. Dick or Iain M. Banks. But by 2015, citizens of the United States may well see these unmanned flying machines patrolling the skies over the homeland. The U.S. government recently pledged to loosen Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) restrictions that would allow local law enforcement agencies to use drones in just a few short years. So, soon the least of your worries will be traffic signal cameras and the local police officer armed with a radar gun. Our home-grown drones are likely to be deployed first for surveillance. But, undoubtedly armaments will follow. Hellfire missiles over Helena, Montana anyone?
[div class=attrib]From National Geographic:[end-div]
At the edge of a stubbly, dried-out alfalfa field outside Grand Junction, Colorado, Deputy Sheriff Derek Johnson, a stocky young man with a buzz cut, squints at a speck crawling across the brilliant, hazy sky. It’s not a vulture or crow but a Falcon—a new brand of unmanned aerial vehicle, or drone, and Johnson is flying it. The sheriff ’s office here in Mesa County, a plateau of farms and ranches corralled by bone-hued mountains, is weighing the Falcon’s potential for spotting lost hikers and criminals on the lam. A laptop on a table in front of Johnson shows the drone’s flickering images of a nearby highway.
Standing behind Johnson, watching him watch the Falcon, is its designer, Chris Miser. Rock-jawed, arms crossed, sunglasses pushed atop his shaved head, Miser is a former Air Force captain who worked on military drones before quitting in 2007 to found his own company in Aurora, Colorado. The Falcon has an eight-foot wingspan but weighs just 9.5 pounds. Powered by an electric motor, it carries two swiveling cameras, visible and infrared, and a GPS-guided autopilot. Sophisticated enough that it can’t be exported without a U.S. government license, the Falcon is roughly comparable, Miser says, to the Raven, a hand-launched military drone—but much cheaper. He plans to sell two drones and support equipment for about the price of a squad car.
A law signed by President Barack Obama in February 2012 directs the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) to throw American airspace wide open to drones by September 30, 2015. But for now Mesa County, with its empty skies, is one of only a few jurisdictions with an FAA permit to fly one. The sheriff ’s office has a three-foot-wide helicopter drone called a Draganflyer, which stays aloft for just 20 minutes.
The Falcon can fly for an hour, and it’s easy to operate. “You just put in the coordinates, and it flies itself,” says Benjamin Miller, who manages the unmanned aircraft program for the sheriff ’s office. To navigate, Johnson types the desired altitude and airspeed into the laptop and clicks targets on a digital map; the autopilot does the rest. To launch the Falcon, you simply hurl it into the air. An accelerometer switches on the propeller only after the bird has taken flight, so it won’t slice the hand that launches it.
The stench from a nearby chicken-processing plant wafts over the alfalfa field. “Let’s go ahead and tell it to land,” Miser says to Johnson. After the deputy sheriff clicks on the laptop, the Falcon swoops lower, releases a neon orange parachute, and drifts gently to the ground, just yards from the spot Johnson clicked on. “The Raven can’t do that,” Miser says proudly.
Offspring of 9/11
A dozen years ago only two communities cared much about drones. One was hobbyists who flew radio-controlled planes and choppers for fun. The other was the military, which carried out surveillance missions with unmanned aircraft like the General Atomics Predator.
Then came 9/11, followed by the U.S. invasions of Afghanistan and Iraq, and drones rapidly became an essential tool of the U.S. armed forces. The Pentagon armed the Predator and a larger unmanned surveillance plane, the Reaper, with missiles, so that their operators—sitting in offices in places like Nevada or New York—could destroy as well as spy on targets thousands of miles away. Aerospace firms churned out a host of smaller drones with increasingly clever computer chips and keen sensors—cameras but also instruments that measure airborne chemicals, pathogens, radioactive materials.
The U.S. has deployed more than 11,000 military drones, up from fewer than 200 in 2002. They carry out a wide variety of missions while saving money and American lives. Within a generation they could replace most manned military aircraft, says John Pike, a defense expert at the think tank GlobalSecurity.org. Pike suspects that the F-35 Lightning II, now under development by Lockheed Martin, might be “the last fighter with an ejector seat, and might get converted into a drone itself.”
At least 50 other countries have drones, and some, notably China, Israel, and Iran, have their own manufacturers. Aviation firms—as well as university and government researchers—are designing a flock of next-generation aircraft, ranging in size from robotic moths and hummingbirds to Boeing’s Phantom Eye, a hydrogen-fueled behemoth with a 150-foot wingspan that can cruise at 65,000 feet for up to four days.
More than a thousand companies, from tiny start-ups like Miser’s to major defense contractors, are now in the drone business—and some are trying to steer drones into the civilian world. Predators already help Customs and Border Protection agents spot smugglers and illegal immigrants sneaking into the U.S. NASA-operated Global Hawks record atmospheric data and peer into hurricanes. Drones have helped scientists gather data on volcanoes in Costa Rica, archaeological sites in Russia and Peru, and flooding in North Dakota.
So far only a dozen police departments, including ones in Miami and Seattle, have applied to the FAA for permits to fly drones. But drone advocates—who generally prefer the term UAV, for unmanned aerial vehicle—say all 18,000 law enforcement agencies in the U.S. are potential customers. They hope UAVs will soon become essential too for agriculture (checking and spraying crops, finding lost cattle), journalism (scoping out public events or celebrity backyards), weather forecasting, traffic control. “The sky’s the limit, pun intended,” says Bill Borgia, an engineer at Lockheed Martin. “Once we get UAVs in the hands of potential users, they’ll think of lots of cool applications.”
The biggest obstacle, advocates say, is current FAA rules, which tightly restrict drone flights by private companies and government agencies (though not by individual hobbyists). Even with an FAA permit, operators can’t fly UAVs above 400 feet or near airports or other zones with heavy air traffic, and they must maintain visual contact with the drones. All that may change, though, under the new law, which requires the FAA to allow the “safe integration” of UAVs into U.S. airspace.
If the FAA relaxes its rules, says Mark Brown, the civilian market for drones—and especially small, low-cost, tactical drones—could soon dwarf military sales, which in 2011 totaled more than three billion dollars. Brown, a former astronaut who is now an aerospace consultant in Dayton, Ohio, helps bring drone manufacturers and potential customers together. The success of military UAVs, he contends, has created “an appetite for more, more, more!” Brown’s PowerPoint presentation is called “On the Threshold of a Dream.”
[div class=attrib]Read the entire article following the jump.[end-div]
[div class=attrib]Image: Unmanned drone used to patrol the U.S.-Canadian border. (U.S. Customs and Border Protection/AP).[end-div]
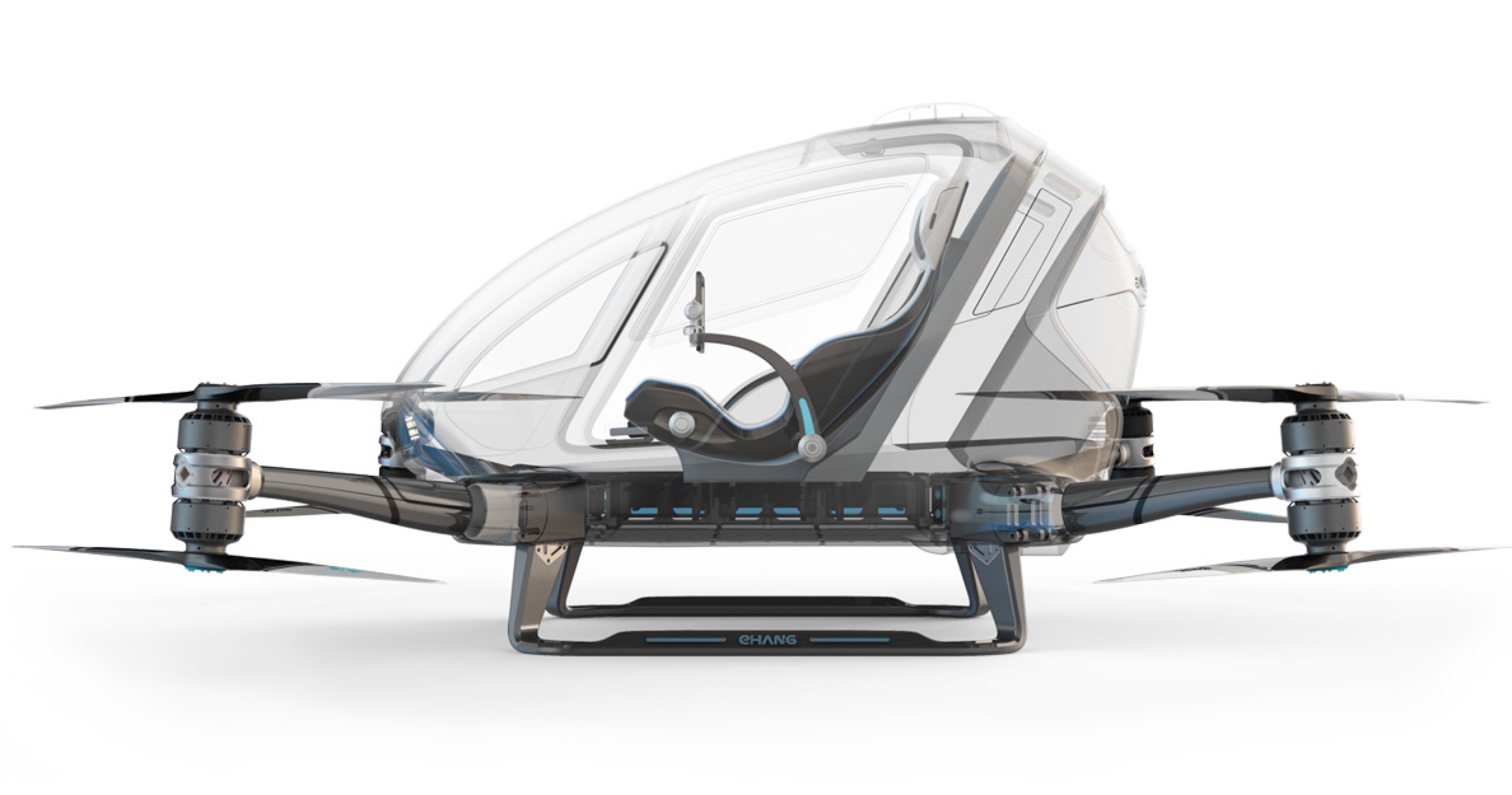

 That said, even though it may still be a few years yet before we see traffic jams of driverless cars clogging the Interstate Highway system, some forward-thinkers are not resting on their laurels.
That said, even though it may still be a few years yet before we see traffic jams of driverless cars clogging the Interstate Highway system, some forward-thinkers are not resting on their laurels. 
 You might expect to find police drones in the pages of a science fiction novel by Philip K. Dick or Iain M. Banks. But by 2015, citizens of the United States may well see these unmanned flying machines patrolling the skies over the homeland. The U.S. government recently pledged to loosen Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) restrictions that would allow local law enforcement agencies to use drones in just a few short years. So, soon the least of your worries will be traffic signal cameras and the local police officer armed with a radar gun. Our home-grown drones are likely to be deployed first for surveillance. But, undoubtedly armaments will follow. Hellfire missiles over Helena, Montana anyone?
You might expect to find police drones in the pages of a science fiction novel by Philip K. Dick or Iain M. Banks. But by 2015, citizens of the United States may well see these unmanned flying machines patrolling the skies over the homeland. The U.S. government recently pledged to loosen Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) restrictions that would allow local law enforcement agencies to use drones in just a few short years. So, soon the least of your worries will be traffic signal cameras and the local police officer armed with a radar gun. Our home-grown drones are likely to be deployed first for surveillance. But, undoubtedly armaments will follow. Hellfire missiles over Helena, Montana anyone?