
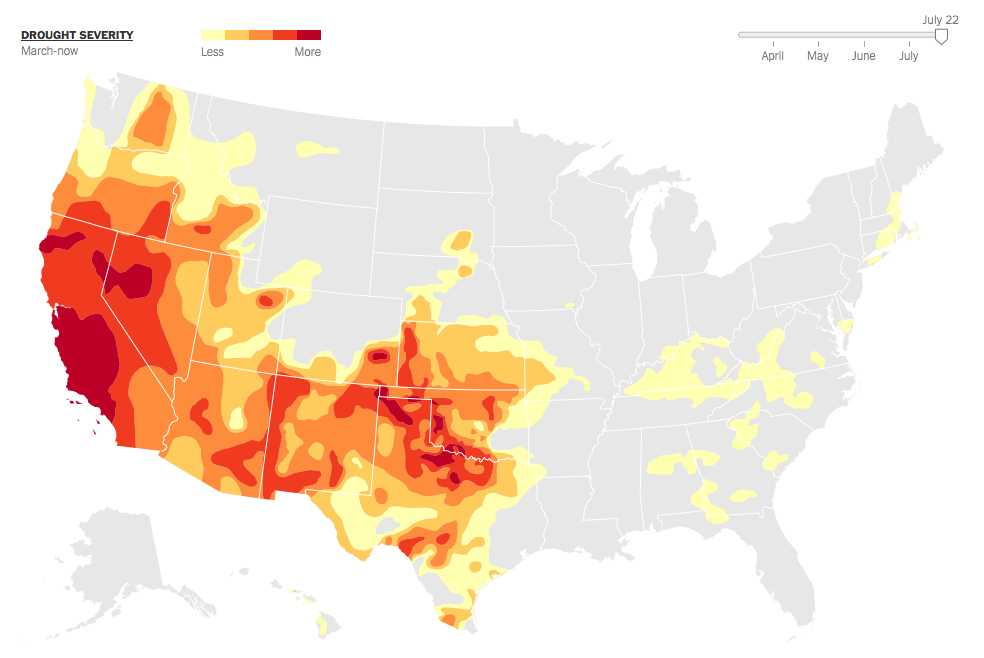
Historians dispute the etymology of the name California. One possible origin comes from the Spanish Catalan phrase which roughly translates as “hot as a lime oven”. But while this may be pure myth there is no doubting the unfolding ecological (and human) disaster caused by incessant heat and lack of water. The severe drought in many parts of the state is now in its third year, and while it is still ongoing it is already recorded as the worst in the last 500 years. The drought is forcing farmers and rural communities to rethink and in some cases resettle, and increasingly it also threatens suburban and urban neighborhoods.
From the NYT:
The punishing drought that has swept California is now threatening the state’s drinking water supply.
With no sign of rain, 17 rural communities providing water to 40,000 people are in danger of running out within 60 to 120 days. State officials said that the number was likely to rise in the months ahead after the State Water Project, the main municipal water distribution system, announced on Friday that it did not have enough water to supplement the dwindling supplies of local agencies that provide water to an additional 25 million people. It is first time the project has turned off its spigot in its 54-year history.
State officials said they were moving to put emergency plans in place. In the worst case, they said drinking water would have to be brought by truck into parched communities and additional wells would have to be drilled to draw on groundwater. The deteriorating situation would likely mean imposing mandatory water conservation measures on homeowners and businesses, who have already been asked to voluntarily reduce their water use by 20 percent.
“Every day this drought goes on we are going to have to tighten the screws on what people are doing” said Gov. Jerry Brown, who was governor during the last major drought here, in 1976-77.
This latest development has underscored the urgency of a drought that has already produced parched fields, starving livestock, and pockets of smog.
“We are on track for having the worst drought in 500 years,” said B. Lynn Ingram, a professor of earth and planetary sciences at the University of California, Berkeley.
Already the drought, technically in its third year, is forcing big shifts in behavior. Farmers in Nevada said they had given up on even planting, while ranchers in Northern California and New Mexico said they were being forced to sell off cattle as fields that should be four feet high with grass are a blanket of brown and stunted stalks.
Fishing and camping in much of California has been outlawed, to protect endangered salmon and guard against fires. Many people said they had already begun to cut back drastically on taking showers, washing their car and watering their lawns.
Rain and snow showers brought relief in parts of the state at the week’s end — people emerging from a movie theater in West Hollywood on Thursday evening broke into applause upon seeing rain splattering on the sidewalk — but they were nowhere near enough to make up for record-long dry stretches, officials said.
“I have experienced a really long career in this area, and my worry meter has never been this high,” said Tim Quinn, executive director of the Association of California Water Agencies, a statewide coalition. “We are talking historical drought conditions, no supplies of water in many parts of the state. My industry’s job is to try to make sure that these kind of things never happen. And they are happening.”
Officials are girding for the kind of geographical, cultural and economic battles that have long plagued a part of the country that is defined by a lack of water: between farmers and environmentalists, urban and rural users, and the northern and southern regions of this state.
“We do have a politics of finger-pointing and blame whenever there is a problem,” said Mr. Brown. “And we have a problem, so there is going to be a tendency to blame people.” President Obama called him last week to check on the drought situation and express his concern.
Tom Vilsack, secretary of the federal Agriculture Department, said in an interview that his agency’s ability to help farmers absorb the shock, with subsidies to buy food for cattle, had been undercut by the long deadlock in Congress over extending the farm bill, which finally seemed to be resolved last week.
Mr. Vilsack called the drought in California a “deep concern,” and a warning sign of trouble ahead for much of the West.
“That’s why it’s important for us to take climate change seriously,” he said. “If we don’t do the research, if we don’t have the financial assistance, if we don’t have the conservation resources, there’s very little we can do to help these farmers.”
The crisis is unfolding in ways expected and unexpected. Near Sacramento, the low level of streams has brought out prospectors, sifting for flecks of gold in slow-running waters. To the west, the heavy water demand of growers of medical marijuana — six gallons per plant per day during a 150-day period — is drawing down streams where salmon and other endangered fish species spawn.
“Every pickup truck has a water tank in the back,” said Scott Bauer, a coho salmon recovery coordinator with the California Department of Fish and Wildlife. “There is a potential to lose whole runs of fish.”
Without rain to scrub the air, pollution in the Los Angeles basin, which has declined over the past decade, has returned to dangerous levels, as evident from the brown-tinged air. Homeowners have been instructed to stop burning wood in their fireplaces.
In the San Joaquin Valley, federal limits for particulate matter were breached for most of December and January. Schools used flags to signal when children should play indoors.
“One of the concerns is that as concentrations get higher, it affects not only the people who are most susceptible, but healthy people as well,” said Karen Magliano, assistant chief of the air quality planning division of the state’s Air Resources Board.
The impact has been particularly severe on farmers and ranchers. “I have friends with the ground torn out, all ready to go,” said Darrell Pursel, who farms just south of Yerington, Nev. “But what are you going to plant? At this moment, it looks like we’re not going to have any water. Unless we get a lot of rain, I know I won’t be planting anything.”
The University of California Cooperative Extension held a drought survival session last week in Browns Valley, about 60 miles north of Sacramento, drawing hundreds of ranchers in person and online. “We have people coming from six or seven hours away,” said Jeffrey James, who ran the session.
Dan Macon, 46, a rancher in Auburn, Calif., said the situation was “as bad as I have ever experienced. Most of our range lands are essentially out of feed.”
With each parched sunrise, a sense of alarm is rising amid signs that this is a drought that comes along only every few centuries. Sacramento had gone 52 days without water, and Albuquerque had gone 42 days without rain or snow as of Saturday.
The snowpack in the Sierra Nevada, which supplies much of California with water during the dry season, was at just 12 percent of normal last week, reflecting the lack of rain or snow in December and January.
Read the entire article here.
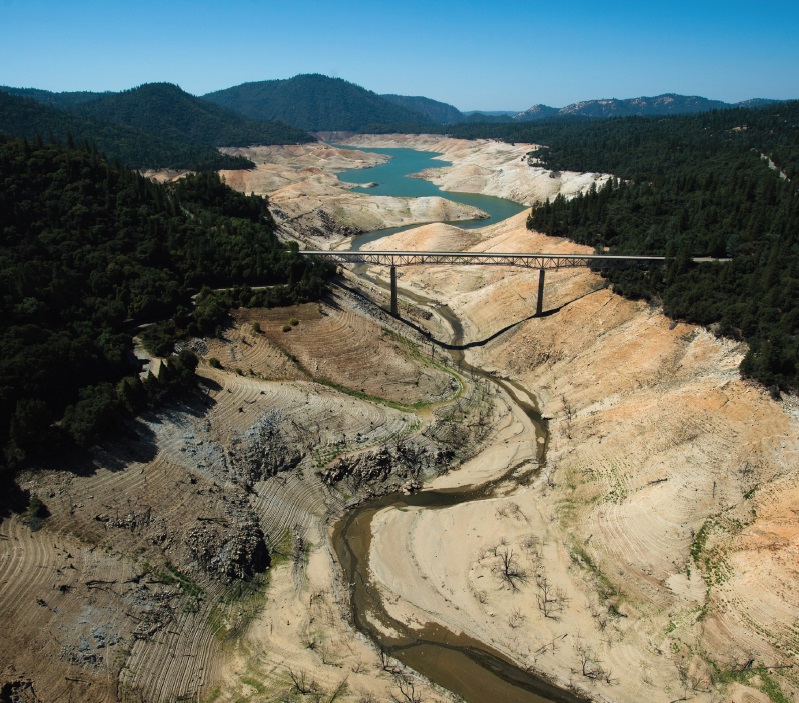
Image: Dry riverbed, Kern River in Bakersfield, California. Courtesy of David McNew/Getty Images / New York Times.
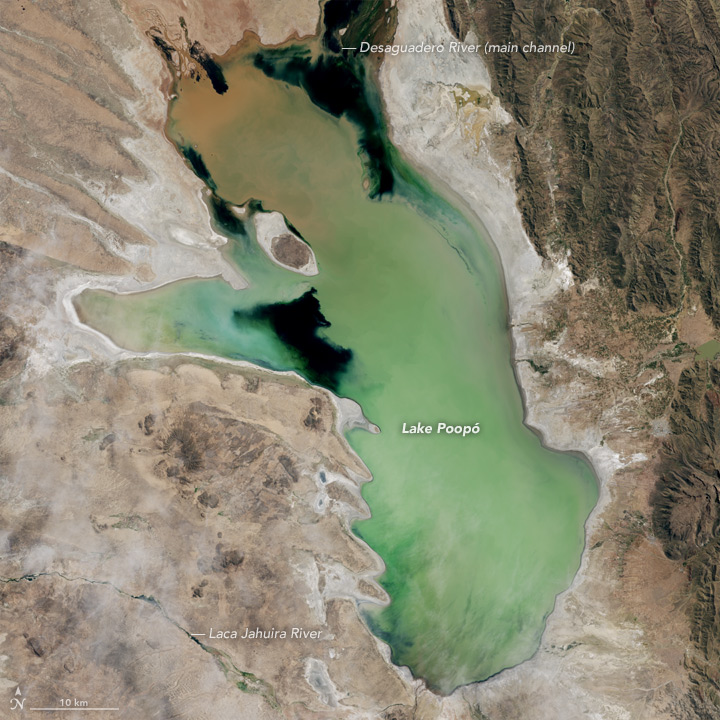
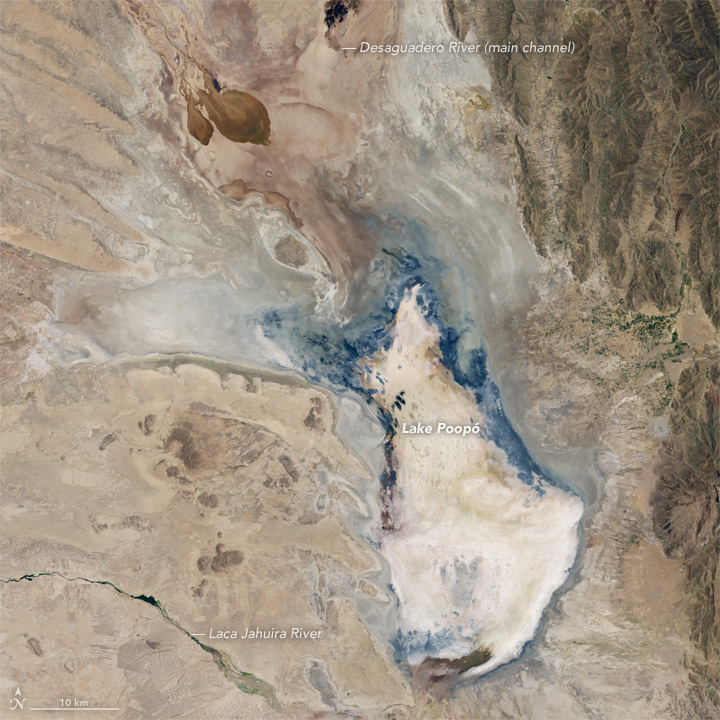
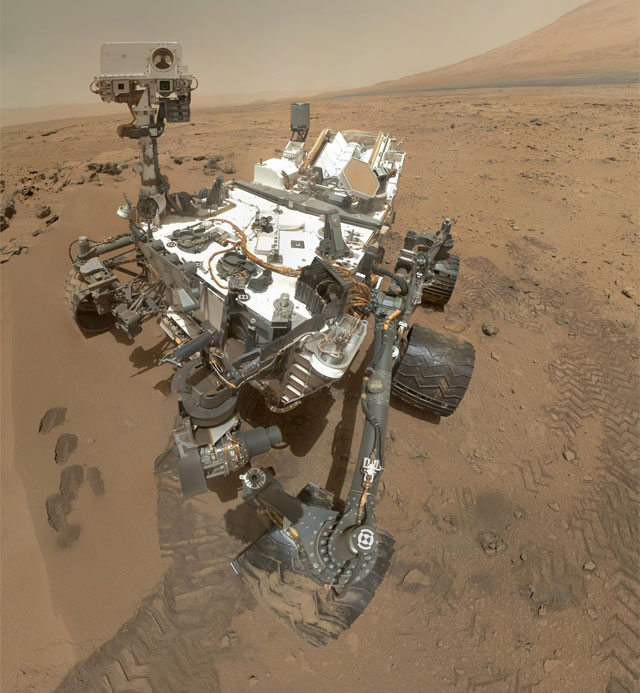










 Curiosity, the latest rover to explore Mars, has found lots of water in the martian soil. Now, it doesn’t run freely, but is chemically bound to other substances. Yet the large volume of H2O bodes well for future human exploration (and settlement).
Curiosity, the latest rover to explore Mars, has found lots of water in the martian soil. Now, it doesn’t run freely, but is chemically bound to other substances. Yet the large volume of H2O bodes well for future human exploration (and settlement).
 Charles Fishman has a fascinating new book entitled The Big Thirst: The Secret Life and Turbulent Future of Water. In it Fishman examines the origins of water on our planet and postulates an all to probable future where water becomes an increasingly limited and precious resource.
Charles Fishman has a fascinating new book entitled The Big Thirst: The Secret Life and Turbulent Future of Water. In it Fishman examines the origins of water on our planet and postulates an all to probable future where water becomes an increasingly limited and precious resource. This week, theDiagonal focuses its energies on that most precious of natural resources — water.
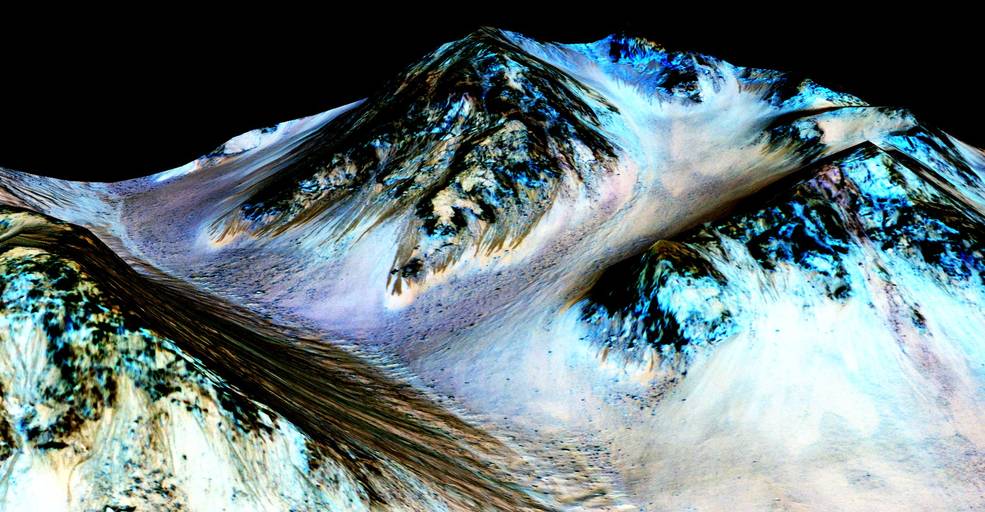
This week, theDiagonal focuses its energies on that most precious of natural resources — water. NASA’s latest spacecraft to visit Mars, the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, has made some stunning observations that show the possibility of flowing water on the red planet. Intriguingly, repeated observations of the same regions over several Martian seasons show visible changes attributable to some kind of dynamic flow.
NASA’s latest spacecraft to visit Mars, the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, has made some stunning observations that show the possibility of flowing water on the red planet. Intriguingly, repeated observations of the same regions over several Martian seasons show visible changes attributable to some kind of dynamic flow.