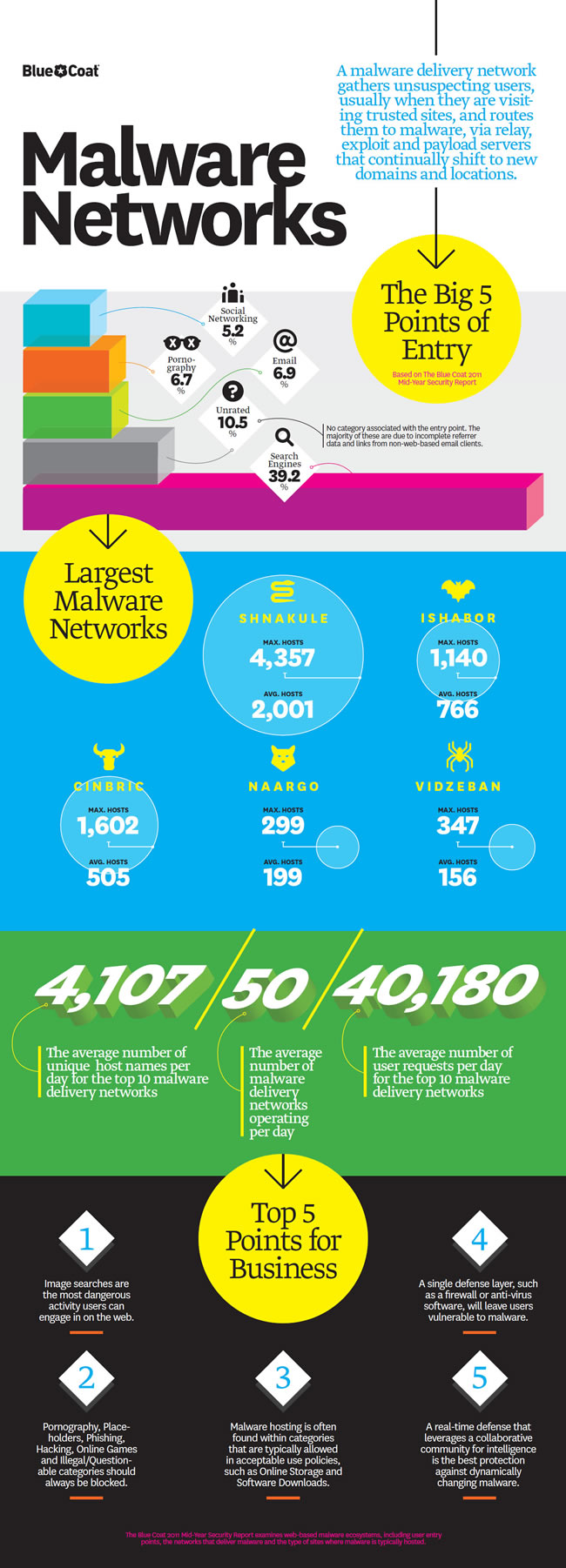
Shnakule, Ishabor, Cinbric, Naargo and Vidzeban are not five fictional colleagues of Lord Voldemort from the mind of JK Rowling. They are indeed bad guys, but they live in our real world, online. Shnakule and its peers are the top 5 malware delivery networks. That is, they host a range of diverse and sophisticated malicious software, or malware, on ever-changing computer networks that seek to avoid detection. Malware on these networks includes: fake anti-virus software, fake software updates, drive-by downloads, suspicious link farming, ransomware, pharmacy spam, malvertising, work-at-home scams and unsolicited pornography. Other malware includes: computer viruses, worms, trojan horses, spyware, dishonest adware, and other unwanted software.
Malware researcher Chris Larsen, with Blue Coat, derived this malware infographic from the company’s Mid-Year Security Report. Interestingly, search engine poisoning is the most prevalent point of entry for the delivery of malware to a user’s computer. As the New York Times reports:
Search engine poisoning (SEP) makes up 40% of malware delivery vectors on the Web. It is easy to see why. People want to be able to trust that what they search for in Google, Bing or Yahoo is safe to click on. Users are not conditioned to think that search results could be harmful to the health of their computers. The other leading attack vectors on the Web all pale in comparison to SEP, with malvertising, email, porn and social networking all 10% of malware delivery.
[div class=attrib]Infographic courtesy of Blue Coat:[end-div]