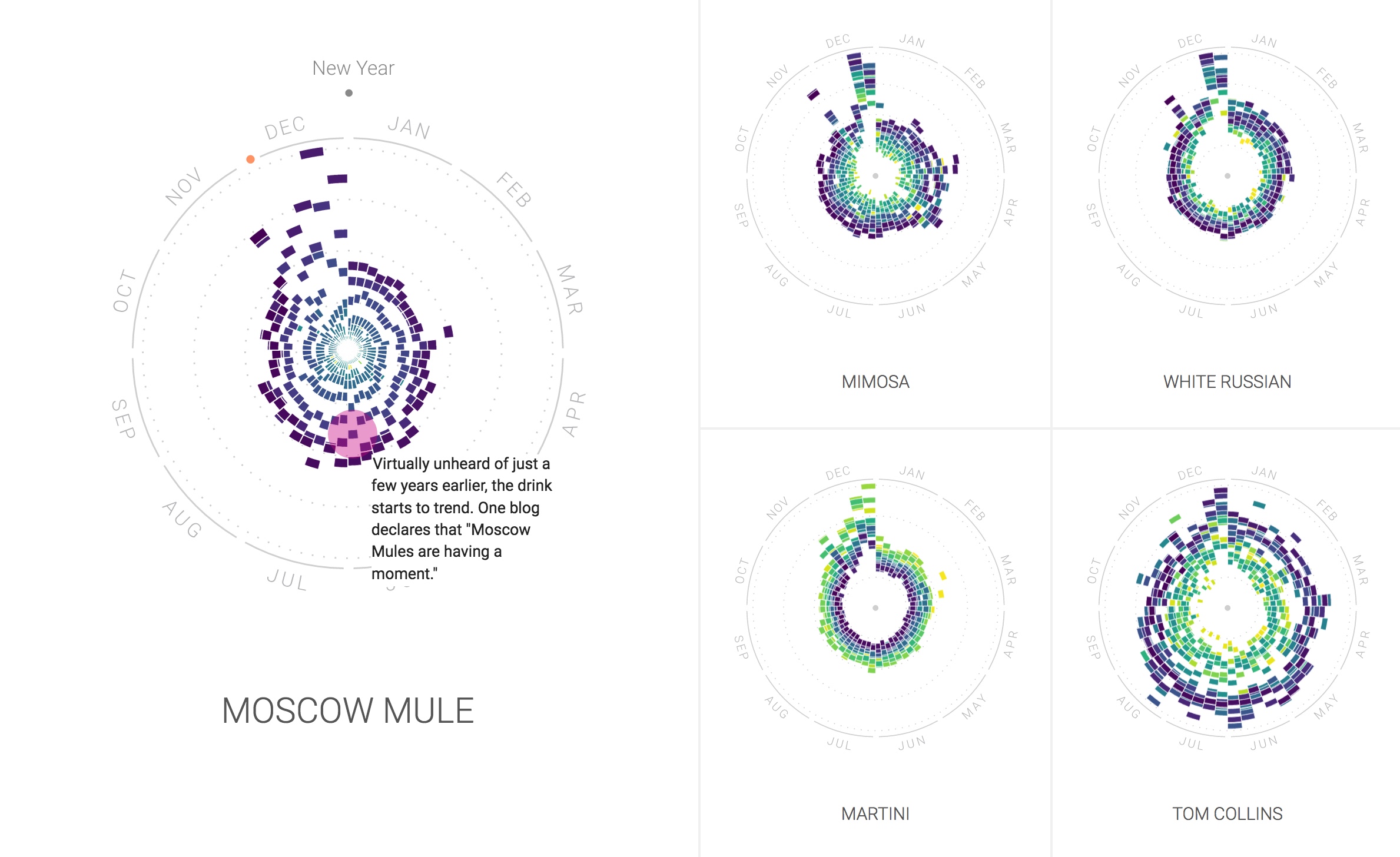
On January 1, 2017, the idea of universal basic income (UBI) took another small but significant leap forward, in Finland.
On January 1, 2017, the idea of universal basic income (UBI) took another small but significant leap forward, in Finland.
UBI is a form of social security where a government institution pays its citizens a regular, unconditional sum.
Finland is testing UBI by handing around $600 per month to 2,000 jobless Finns for the next two years. It’s a bold experiment aimed at helping the long-term unemployed.
From Business Insider:
Finland has an ambitious New Year’s resolution in mind: learn how offering free money for two years helps the unemployed get back to work.
Starting January 1, 2017 and lasting until 2019, the federal social security institution Kela will distribute roughly $590 each month to 2,000 jobless Finns.
Regardless of whether they find work during that period, the money will keep coming in at the beginning of each month — a trial version of basic income, one of the past year’s most popular theories of how to solve poverty.
Under universal basic income (UBI), people receive a standard amount of money just for being alive. By handing out the money to everyone, regardless of their income status, UBI advocates say the system prevents people from falling through the cracks.
Marjukka Turunen, head of Kela’s legal benefits unit, says the experiment in Finland should provide insights on two fronts.
The first is whether basic income could help clean up Finland’s messy system of social security. Depending on their specific needs, Turunen says residents could be on one of 40 different benefit systems. Each benefit — whether it’s for someone who’s sick, unemployed, a student, or so on— is calculated differently and must be changed when the person’s status changes.
“That’s really a burden for customers and Kela to do all those status changes,” Turunen tells Business Insider. A form of basic income could mean people just need to apply for one status indefinitely, no changes required.
The experiment will also provide clues about how people behave when they’re receiving free money. Skeptics say people will sit on their couch all day. Proponents claim they’ll actually use the money to make their lives better. (Limited evidence from developing countries suggests it’s more of the latter.)
Turunen suspects the experiment will compel at least a few wannabe entrepreneurs to make the leap into starting their own business — a risky proposition in Finland today since business owners who are forced to close shop don’t receive unemployment benefits. It’s not unlike the system in place in most US states.
Read the entire story here.
Image: Finland coat of arms. Courtesy: / Wipipedia. Public Domain.

 We all need heroes. So, if you wish to become one, you would stand a better chance if you took your dying breaths atop a hill. Also, it would really help your cause if you arrived via virgin birth.
We all need heroes. So, if you wish to become one, you would stand a better chance if you took your dying breaths atop a hill. Also, it would really help your cause if you arrived via virgin birth.