
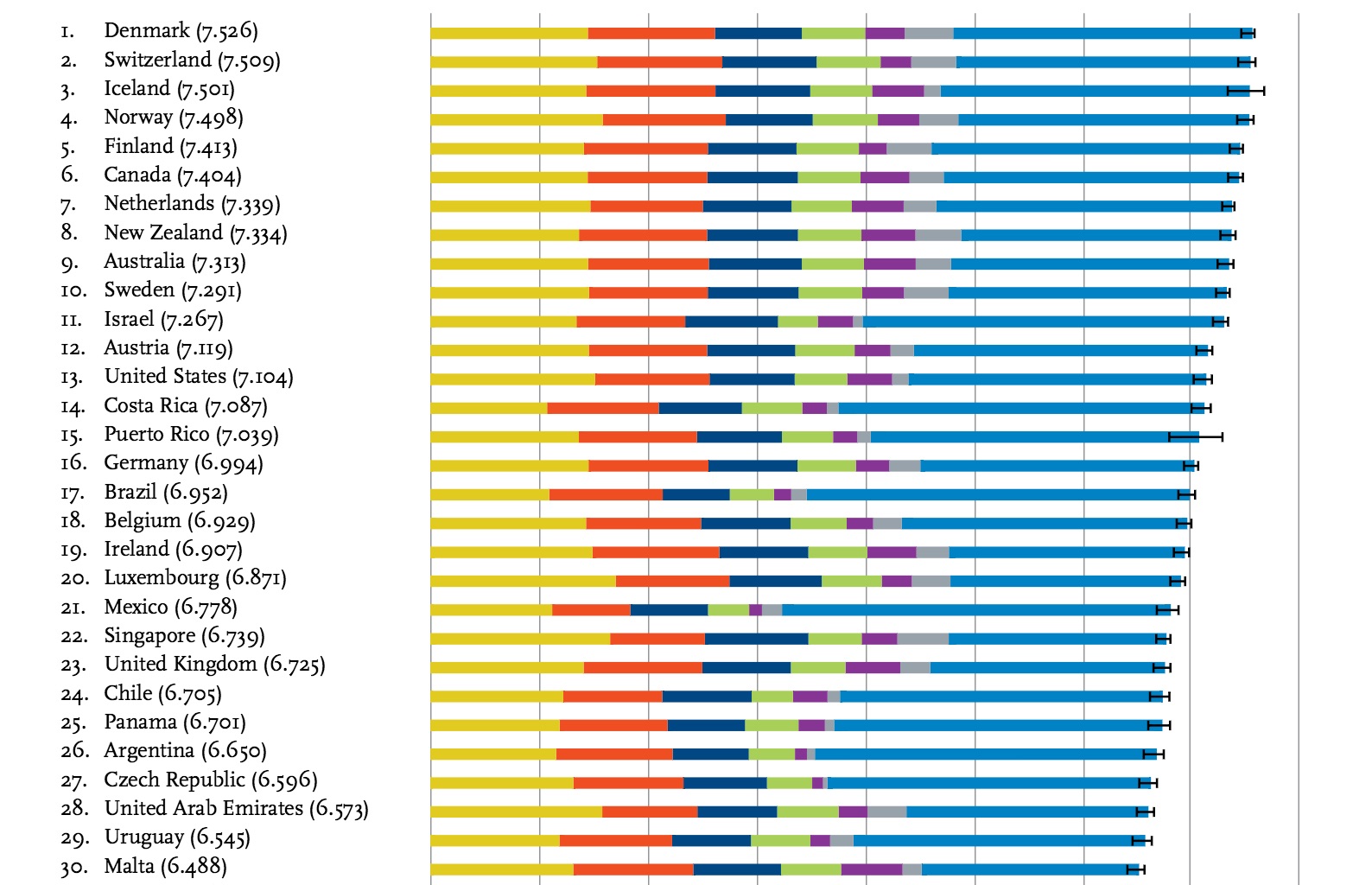
Trust the Danes to come up with it. Survey after survey often puts Denmark at or near the top of global happiness rankings. Followers of all things happiness put this national contentment down to an ethereal quality known as “hygge“. Just as with most recipes for happiness, hygge is rather difficult to define, but generally I would characterize it as “informal, public coziness with a touch of self-indulgence.” The Danes must know a little about happiness — after all, they did invent Lego.
From the Guardian:
Jeppe Trolle Linnet’s gaze dances around Bang & Jensen, his favourite Copenhagen café-bar, seeking out anything and everything that brings it hygge, that untranslatable quality of places, people and togetherness prized by Danes above almost all else.
“It’s the candles, obviously … the lighting. It’s not like they have big lamps on the ceiling,” he says. Then the furnishings: “You get the feeling that, ‘hmm, this must have been brought in from various places’.” He gestures at the flip-down seats we’re sitting on. “Like an old cinema. So probably someone knew someone. Just by the look of it, it suggests that people here are connected to someone, so the whole place is full of sociality, even when it’s empty.” He rubs the shiny brass where his feet are resting. “And obviously it’s all pretty worn, you feel that if you put your feet up, it wouldn’t really matter.”
Linnet published the first academic paper on hygge five years ago, since when he has become the go-to expert for Danish journalists, particularly around Christmas, when hygge is paramount.
If this is the first you’ve heard of hygge, pronounced “hue-guh” and usually translated as “cosiness”, you are about to hear a whole lot more.
Five books on the subject are hitting the shelves this autumn. There’s The Little Book of Hygge by Meik Wiking (subtitled “The Danish way to live well”), out last week. And The Book of Hygge by Louisa Thomsen Brits (subtitled “The Danish art of living well”), out last month. Coming later this week is The Art of Hygge, while How to Hygge and Hygge: A Celebration of Simple Pleasures, Living the Danish Way, are both out next month.
“It’s the new black,” laughs Agnete Wulff, whose husband Poul owns Wulff & Konstali Food Shop, reputedly the Danish capital’s most hygge place for breakfast, where I drop in first thing in the morning.
Read the entire story here.
Image: Nyhavn, a 17th-century waterfront lined by brightly colored townhouses, Copenhagen, Denmark. Courtesy: GuoJunjun / Wikipedia.
CC BY-SA 3.0.

 [div class=attrib]From the New York Times:[end-div]
[div class=attrib]From the New York Times:[end-div]