Surely there is intelligent life somewhere in the universe. Cosmologists estimate that the observable universe contains around 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 planets. And, they calculate that our Milky Way galaxy alone contains around 100 billion planets that are hospitable to life (as we currently know it).
These numbers boggle the mind and beg a question: how do we find evidence for life beyond our shores? The decades long search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI) pioneered the use of radio telescope observations to look for alien signals from deep space. But, the process has remained rather rudimentary and narrowly focused. The good news now is that astronomers and astrobiologists have a growing toolkit of techniques that allow for much more sophisticated detection and analysis of the broader signals of life — not just potential radio transmissions from an advanced alien culture.
From Quanta:
Huddled in a coffee shop one drizzly Seattle morning six years ago, the astrobiologist Shawn Domagal-Goldman stared blankly at his laptop screen, paralyzed. He had been running a simulation of an evolving planet, when suddenly oxygen started accumulating in the virtual planet’s atmosphere. Up the concentration ticked, from 0 to 5 to 10 percent.
“Is something wrong?” his wife asked.
“Yeah.”
The rise of oxygen was bad news for the search for extraterrestrial life.
After millennia of wondering whether we’re alone in the universe — one of “mankind’s most profound and probably earliest questions beyond, ‘What are you going to have for dinner?’” as the NASA astrobiologist Lynn Rothschild put it — the hunt for life on other planets is now ramping up in a serious way. Thousands of exoplanets, or planets orbiting stars other than the sun, have been discovered in the past decade. Among them are potential super-Earths, sub-Neptunes, hot Jupiters and worlds such as Kepler-452b, a possibly rocky, watery “Earth cousin” located 1,400 light-years from here. Starting in 2018 with the expected launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, astronomers will be able to peer across the light-years and scope out the atmospheres of the most promising exoplanets. They will look for the presence of “biosignature gases,” vapors that could only be produced by alien life.
They’ll do this by observing the thin ring of starlight around an exoplanet while it is positioned in front of its parent star. Gases in the exoplanet’s atmosphere will absorb certain frequencies of the starlight, leaving telltale dips in the spectrum.
As Domagal-Goldman, then a researcher at the University of Washington’s Virtual Planetary Laboratory (VPL), well knew, the gold standard in biosignature gases is oxygen. Not only is oxygen produced in abundance by Earth’s flora — and thus, possibly, other planets’ — but 50 years of conventional wisdom held that it could not be produced at detectable levels by geology or photochemistry alone, making it a forgery-proof signature of life. Oxygen filled the sky on Domagal-Goldman’s simulated world, however, not as a result of biological activity there, but because extreme solar radiation was stripping oxygen atoms off carbon dioxide molecules in the air faster than they could recombine. This biosignature could be forged after all.
The search for biosignature gases around faraway exoplanets “is an inherently messy problem,” said Victoria Meadows, an Australian powerhouse who heads VPL. In the years since Domagal-Goldman’s discovery, Meadows has charged her team of 75 with identifying the major “oxygen false positives” that can arise on exoplanets, as well as ways to distinguish these false alarms from true oxygenic signs of biological activity. Meadows still thinks oxygen is the best biosignature gas. But, she said, “if I’m going to look for this, I want to make sure that when I see it, I know what I’m seeing.”
Meanwhile, Sara Seager, a dogged hunter of “twin Earths” at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology who is widely credited with inventing the spectral technique for analyzing exoplanet atmospheres, is pushing research on biosignature gases in a different direction. Seager acknowledges that oxygen is promising, but she urges the astrobiology community to be less terra-centric in its view of how alien life might operate — to think beyond Earth’s geochemistry and the particular air we breathe. “My view is that we do not want to leave a single stone unturned; we need to consider everything,” she said.
As future telescopes widen the survey of Earth-like worlds, it’s only a matter of time before a potential biosignature gas is detected in a faraway sky. It will look like the discovery of all time: evidence that we are not alone. But how will we know for sure?
Read the entire article here.
Image: Artist’s Impression of Gliese 581 c, the first terrestrial extrasolar planet discovered within its star’s habitable zone. Courtesy: Hervé Piraud, Latitude0116, Xhienne. Creative Commons Attribution 2.5.

 I’m not quite sure when the era of political correctness died, but surely our current election cycle truly signals its end. The pendulum of discourse has now swung fully away from PC to PS — Political Shamelessness.
I’m not quite sure when the era of political correctness died, but surely our current election cycle truly signals its end. The pendulum of discourse has now swung fully away from PC to PS — Political Shamelessness.


 Many political scholars, commentators and members of the public — of all political stripes — who remember
Many political scholars, commentators and members of the public — of all political stripes — who remember 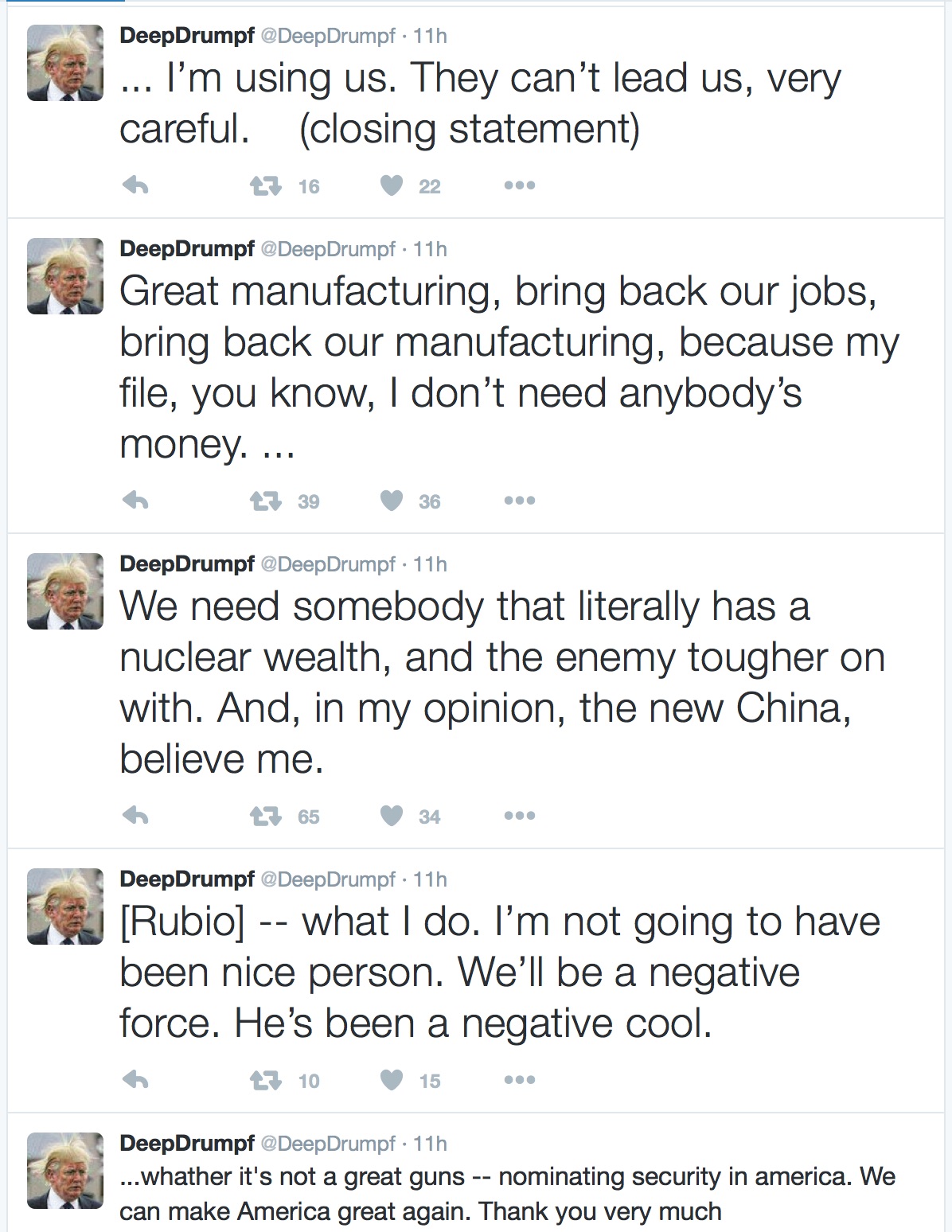



 Ever had that curious tingling sensation at the back and base of your neck? Of course you have. Perhaps you’ve felt this sensation during a particular piece of music or from a watching a key scene in a movie or when taking in a panorama from the top of a mountain or from smelling a childhood aroma again. In fact, most people report having felt this sensation, albeit rather infrequently.
Ever had that curious tingling sensation at the back and base of your neck? Of course you have. Perhaps you’ve felt this sensation during a particular piece of music or from a watching a key scene in a movie or when taking in a panorama from the top of a mountain or from smelling a childhood aroma again. In fact, most people report having felt this sensation, albeit rather infrequently.