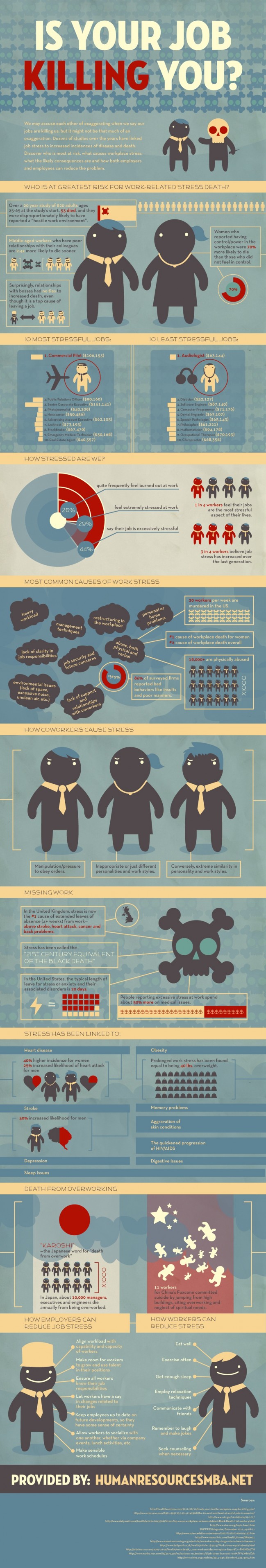
Amazon was supposed to give you back precious time by making shopping and spending painlessly simple. Apps on your smartphone were supposed to do the same for all manner of re-tooled on-demand services. What wonderful time-saving inventions! So, now you can live in the moment and make use of all this extra free time. It’s your time now. You’ve won it back and no one can take it away.
And, what do you spend this newly earned free time doing? Well, you sit at home in your isolated cocoon, you shop for more things online, you download some more great apps that promise to bring even greater convenience, you interact less with real humans, and, best of all, you spend more time working. Welcome to your new dystopian nightmare, and it’s happening right now. Click.
From Medium:
Angel the concierge stands behind a lobby desk at a luxe apartment building in downtown San Francisco, and describes the residents of this imperial, 37-story tower. “Ubers, Squares, a few Twitters,” she says. “A lot of work-from-homers.”
And by late afternoon on a Tuesday, they’re striding into the lobby at a just-get-me-home-goddammit clip, some with laptop bags slung over their shoulders, others carrying swank leather satchels. At the same time a second, temporary population streams into the building: the app-based meal delivery people hoisting thermal carrier bags and sacks. Green means Sprig. A huge M means Munchery. Down in the basement, Amazon Prime delivery people check in packages with the porter. The Instacart groceries are plunked straight into a walk-in fridge.
This is a familiar scene. Five months ago I moved into a spartan apartment a few blocks away, where dozens of startups and thousands of tech workers live. Outside my building there’s always a phalanx of befuddled delivery guys who seem relieved when you walk out, so they can get in. Inside, the place is stuffed with the goodies they bring: Amazon Prime boxes sitting outside doors, evidence of the tangible, quotidian needs that are being serviced by the web. The humans who live there, though, I mostly never see. And even when I do, there seems to be a tacit agreement among residents to not talk to one another. I floated a few “hi’s” in the elevator when I first moved in, but in return I got the monosyllabic, no-eye-contact mumble. It was clear: Lady, this is not that kind of building.
Back in the elevator in the 37-story tower, the messengers do talk, one tells me. They end up asking each other which apps they work for: Postmates. Seamless. EAT24. GrubHub. Safeway.com. A woman hauling two Whole Foods sacks reads the concierge an apartment number off her smartphone, along with the resident’s directions: “Please deliver to my door.”
“They have a nice kitchen up there,” Angel says. The apartments rent for as much as $5,000 a month for a one-bedroom. “But so much, so much food comes in. Between 4 and 8 o’clock, they’re on fire.”
I start to walk toward home. En route, I pass an EAT24 ad on a bus stop shelter, and a little further down the street, a Dungeons & Dragons–type dude opens the locked lobby door of yet another glass-box residential building for a Sprig deliveryman:
“You’re…”
“Jonathan?”
“Sweet,” Dungeons & Dragons says, grabbing the bag of food. The door clanks behind him.
And that’s when I realized: the on-demand world isn’t about sharing at all. It’s about being served. This is an economy of shut-ins.
In 1998, Carnegie Mellon researchers warned that the internet could make us into hermits. They released a study monitoring the social behavior of 169 people making their first forays online. The web-surfers started talking less with family and friends, and grew more isolated and depressed. “We were surprised to find that what is a social technology has such anti-social consequences,” said one of the researchers at the time. “And these are the same people who, when asked, describe the Internet as a positive thing.”
We’re now deep into the bombastic buildout of the on-demand economy— with investment in the apps, platforms and services surging exponentially. Right now Americans buy nearly eight percent of all their retail goods online, though that seems a wild underestimate in the most congested, wired, time-strapped urban centers.
Many services promote themselves as life-expanding?—?there to free up your time so you can spend it connecting with the people you care about, not standing at the post office with strangers. Rinse’s ad shows a couple chilling at a park, their laundry being washed by someone, somewhere beyond the picture’s frame. But plenty of the delivery companies are brutally honest that, actually, they never want you to leave home at all.
GrubHub’s advertising banks on us secretly never wanting to talk to a human again: “Everything great about eating, combined with everything great about not talking to people.” DoorDash, another food delivery service, goes for the all-caps, batshit extreme:
“NEVER LEAVE HOME AGAIN.”
Katherine van Ekert isn’t a shut-in, exactly, but there are only two things she ever has to run errands for any more: trash bags and saline solution. For those, she must leave her San Francisco apartment and walk two blocks to the drug store, “so woe is my life,” she tells me. (She realizes her dry humor about #firstworldproblems may not translate, and clarifies later: “Honestly, this is all tongue in cheek. We’re not spoiled brats.”) Everything else is done by app. Her husband’s office contracts with Washio. Groceries come from Instacart. “I live on Amazon,” she says, buying everything from curry leaves to a jogging suit for her dog, complete with hoodie.
She’s so partial to these services, in fact, that she’s running one of her own: A veterinarian by trade, she’s a co-founder of VetPronto, which sends an on-call vet to your house. It’s one of a half-dozen on-demand services in the current batch at Y Combinator, the startup factory, including a marijuana delivery app called Meadow (“You laugh, but they’re going to be rich,” she says). She took a look at her current clients?—?they skew late 20s to late 30s, and work in high-paying jobs: “The kinds of people who use a lot of on demand services and hang out on Yelp a lot ?”
Basically, people a lot like herself. That’s the common wisdom: the apps are created by the urban young for the needs of urban young. The potential of delivery with a swipe of the finger is exciting for van Ekert, who grew up without such services in Sydney and recently arrived in wired San Francisco. “I’m just milking this city for all it’s worth,” she says. “I was talking to my father on Skype the other day. He asked, ‘Don’t you miss a casual stroll to the shop?’ Everything we do now is time-limited, and you do everything with intention. There’s not time to stroll anywhere.”
Suddenly, for people like van Ekert, the end of chores is here. After hours, you’re free from dirty laundry and dishes. (TaskRabbit’s ad rolls by me on a bus: “Buy yourself time?—?literally.”)
So here’s the big question. What does she, or you, or any of us do with all this time we’re buying? Binge on Netflix shows? Go for a run? Van Ekert’s answer: “It’s more to dedicate more time to working.”
Read the entire story here.











 Gary Gutting, professor of philosophy at the University of Notre Dame reminds us that work is punishment for Adam’s sin, according to the Book of Genesis. No doubt, many who hold other faiths, as well as those who don’t, may tend to agree with this basic notion.
Gary Gutting, professor of philosophy at the University of Notre Dame reminds us that work is punishment for Adam’s sin, according to the Book of Genesis. No doubt, many who hold other faiths, as well as those who don’t, may tend to agree with this basic notion. Apparently, being busy alleviates the human existential threat. So, if your roughly 16 hours, or more, of wakefulness each day is crammed with memos, driving, meetings, widgets, calls, charts, quotas, angry customers, school lunches, deciding, reports, bank statements, kids, budgets, bills, baking, making, fixing, cleaning and mad bosses, then your life must be meaningful, right?
Apparently, being busy alleviates the human existential threat. So, if your roughly 16 hours, or more, of wakefulness each day is crammed with memos, driving, meetings, widgets, calls, charts, quotas, angry customers, school lunches, deciding, reports, bank statements, kids, budgets, bills, baking, making, fixing, cleaning and mad bosses, then your life must be meaningful, right?