 Since they were first dreamed up explanations of the very small (quantum mechanics) and the very large (general relativity) have both been highly successful at describing their respective spheres of influence. Yet, these two descriptions of our physical universe are not compatible, particularly when it comes to describing gravity. Indeed, physicists and theorists have struggled for decades to unite these two frameworks. Many agree that we need a new theory (of everything).
Since they were first dreamed up explanations of the very small (quantum mechanics) and the very large (general relativity) have both been highly successful at describing their respective spheres of influence. Yet, these two descriptions of our physical universe are not compatible, particularly when it comes to describing gravity. Indeed, physicists and theorists have struggled for decades to unite these two frameworks. Many agree that we need a new theory (of everything).
One new idea, from theorist Erik Verlinde of the University of Amsterdam, proposes that time is an emergent construct (it’s not a fundamental building block) and that dark matter is an illusion.
From Quanta:
Theoretical physicists striving to unify quantum mechanics and general relativity into an all-encompassing theory of quantum gravity face what’s called the “problem of time.”
In quantum mechanics, time is universal and absolute; its steady ticks dictate the evolving entanglements between particles. But in general relativity (Albert Einstein’s theory of gravity), time is relative and dynamical, a dimension that’s inextricably interwoven with directions x, y and z into a four-dimensional “space-time” fabric. The fabric warps under the weight of matter, causing nearby stuff to fall toward it (this is gravity), and slowing the passage of time relative to clocks far away. Or hop in a rocket and use fuel rather than gravity to accelerate through space, and time dilates; you age less than someone who stayed at home.
Unifying quantum mechanics and general relativity requires reconciling their absolute and relative notions of time. Recently, a promising burst of research on quantum gravity has provided an outline of what the reconciliation might look like — as well as insights on the true nature of time.
As I described in an article this week on a new theoretical attempt to explain away dark matter, many leading physicists now consider space-time and gravity to be “emergent” phenomena: Bendy, curvy space-time and the matter within it are a hologram that arises out of a network of entangled qubits (quantum bits of information), much as the three-dimensional environment of a computer game is encoded in the classical bits on a silicon chip. “I think we now understand that space-time really is just a geometrical representation of the entanglement structure of these underlying quantum systems,” said Mark Van Raamsdonk, a theoretical physicist at the University of British Columbia.
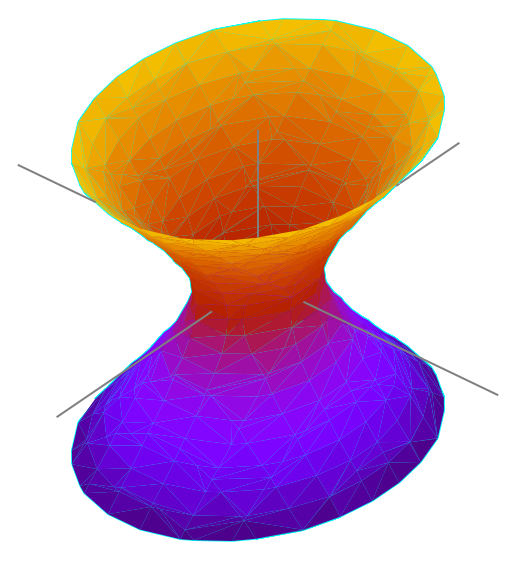
Researchers have worked out the math showing how the hologram arises in toy universes that possess a fisheye space-time geometry known as “anti-de Sitter” (AdS) space. In these warped worlds, spatial increments get shorter and shorter as you move out from the center. Eventually, the spatial dimension extending from the center shrinks to nothing, hitting a boundary. The existence of this boundary — which has one fewer spatial dimension than the interior space-time, or “bulk” — aids calculations by providing a rigid stage on which to model the entangled qubits that project the hologram within. “Inside the bulk, time starts bending and curving with the space in dramatic ways,” said Brian Swingle of Harvard and Brandeis universities. “We have an understanding of how to describe that in terms of the ‘sludge’ on the boundary,” he added, referring to the entangled qubits.
The states of the qubits evolve according to universal time as if executing steps in a computer code, giving rise to warped, relativistic time in the bulk of the AdS space. The only thing is, that’s not quite how it works in our universe.
Here, the space-time fabric has a “de Sitter” geometry, stretching as you look into the distance. The fabric stretches until the universe hits a very different sort of boundary from the one in AdS space: the end of time. At that point, in an event known as “heat death,” space-time will have stretched so much that everything in it will become causally disconnected from everything else, such that no signals can ever again travel between them. The familiar notion of time breaks down. From then on, nothing happens.
On the timeless boundary of our space-time bubble, the entanglements linking together qubits (and encoding the universe’s dynamical interior) would presumably remain intact, since these quantum correlations do not require that signals be sent back and forth. But the state of the qubits must be static and timeless. This line of reasoning suggests that somehow, just as the qubits on the boundary of AdS space give rise to an interior with one extra spatial dimension, qubits on the timeless boundary of de Sitter space must give rise to a universe with time — dynamical time, in particular. Researchers haven’t yet figured out how to do these calculations. “In de Sitter space,” Swingle said, “we don’t have a good idea for how to understand the emergence of time.”
Read the entire article here.
Image: Image of (1 + 1)-dimensional anti-de Sitter space embedded in flat (1 + 2)-dimensional space. The t1- and t2-axes lie in the plane of rotational symmetry, and the x1-axis is normal to that plane. The embedded surface contains closed timelike curves circling the x1 axis, though these can be eliminated by “unrolling” the embedding (more precisely, by taking the universal cover). Courtesy: Krishnavedala. Wikipedia. Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0.



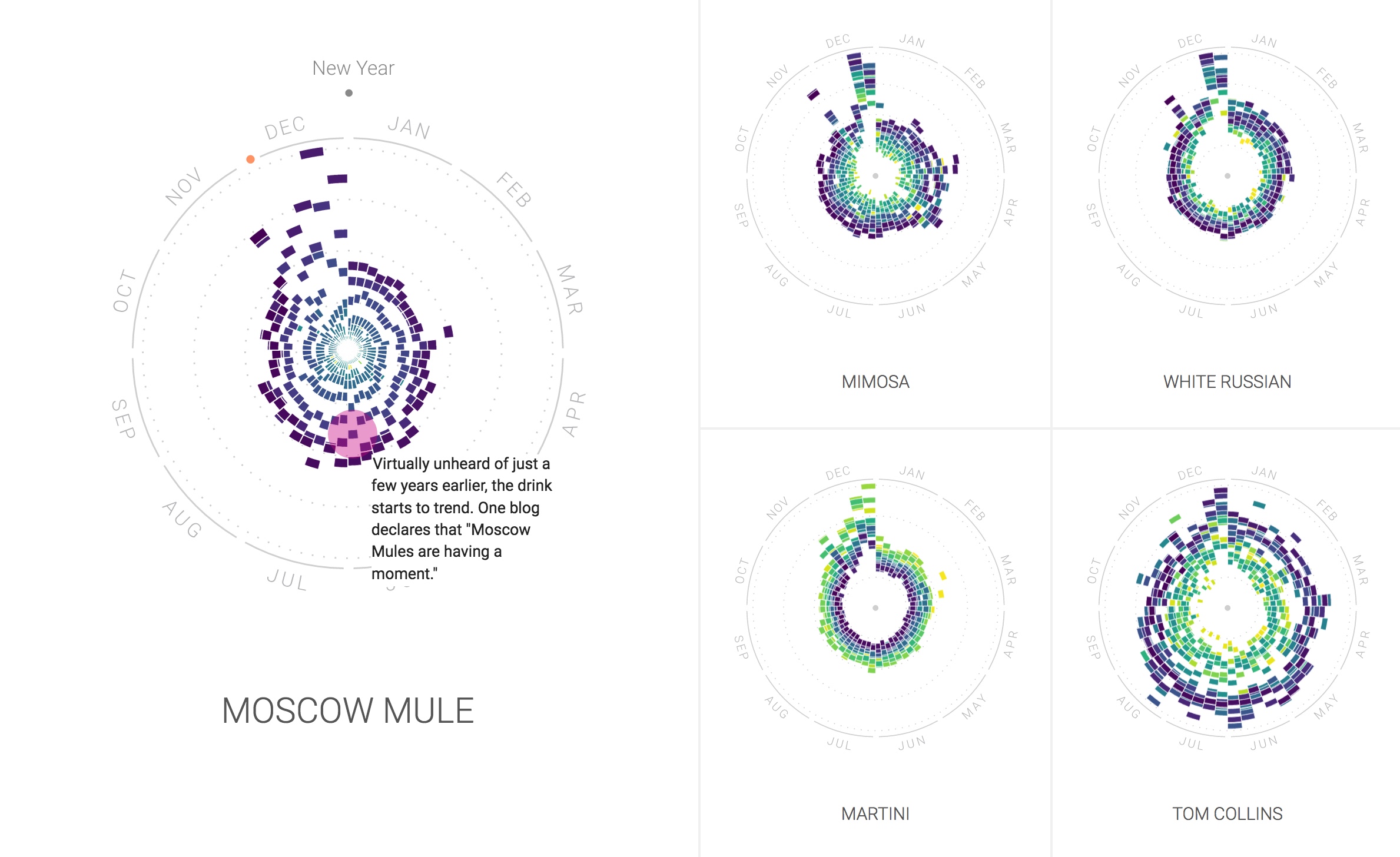
 On January 1, 2017, the idea of
On January 1, 2017, the idea of 


 We all need heroes. So, if you wish to become one, you would stand a better chance if you took your dying breaths atop a hill. Also, it would really help your cause if you arrived via virgin birth.
We all need heroes. So, if you wish to become one, you would stand a better chance if you took your dying breaths atop a hill. Also, it would really help your cause if you arrived via virgin birth.



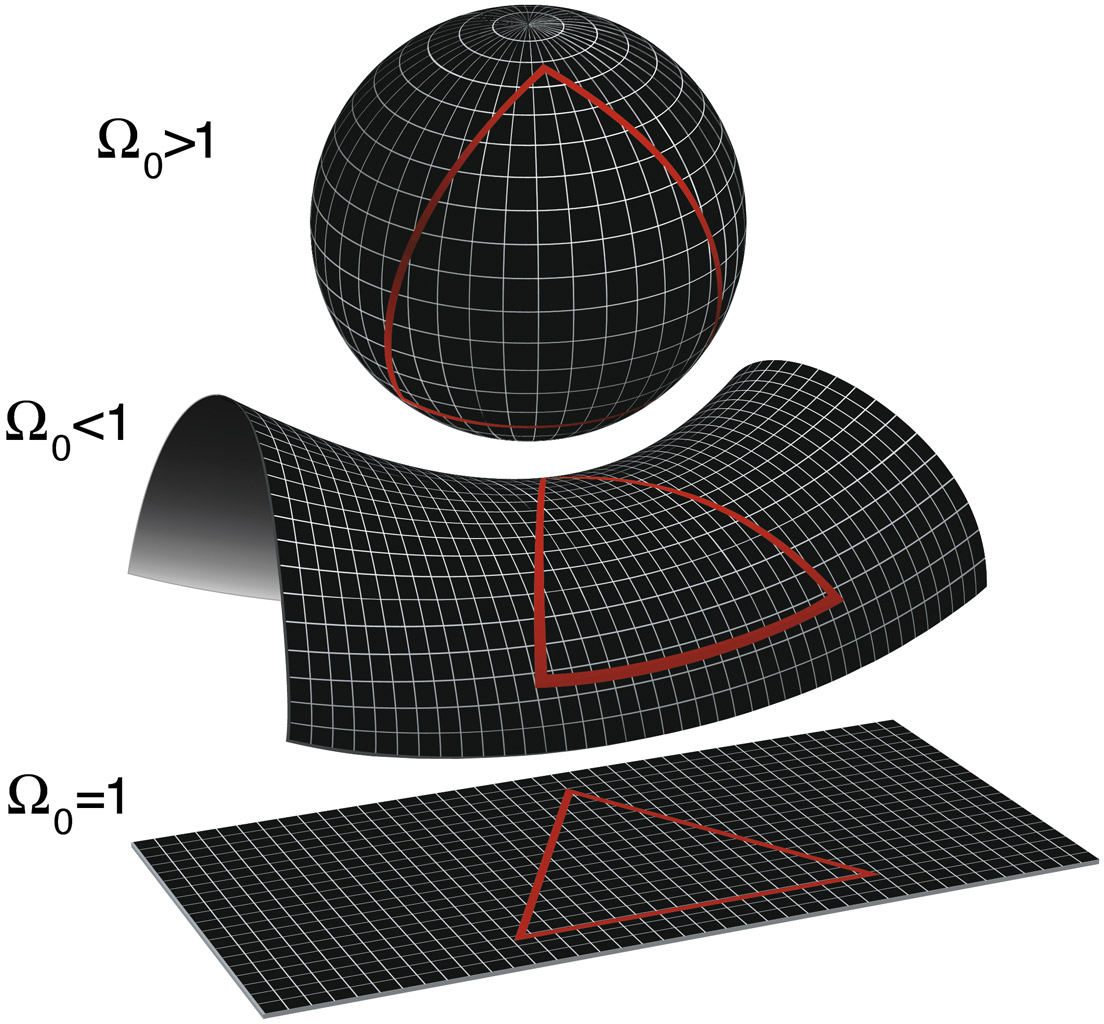
 Since they were first dreamed up explanations of the very small (quantum mechanics) and the very large (general relativity) have both been highly successful at describing their respective spheres of influence. Yet, these two descriptions of our physical universe are not compatible, particularly when it comes to describing gravity. Indeed, physicists and theorists have struggled for decades to unite these two frameworks. Many agree that we need a new theory (of everything).
Since they were first dreamed up explanations of the very small (quantum mechanics) and the very large (general relativity) have both been highly successful at describing their respective spheres of influence. Yet, these two descriptions of our physical universe are not compatible, particularly when it comes to describing gravity. Indeed, physicists and theorists have struggled for decades to unite these two frameworks. Many agree that we need a new theory (of everything).
 What do you get when you set AI (artificial intelligence) the task of reading through 30,000 Danish folk and fairy tales? Well, you get a host of fascinating, newly discovered insights into Scandinavian witches and trolls.
What do you get when you set AI (artificial intelligence) the task of reading through 30,000 Danish folk and fairy tales? Well, you get a host of fascinating, newly discovered insights into Scandinavian witches and trolls.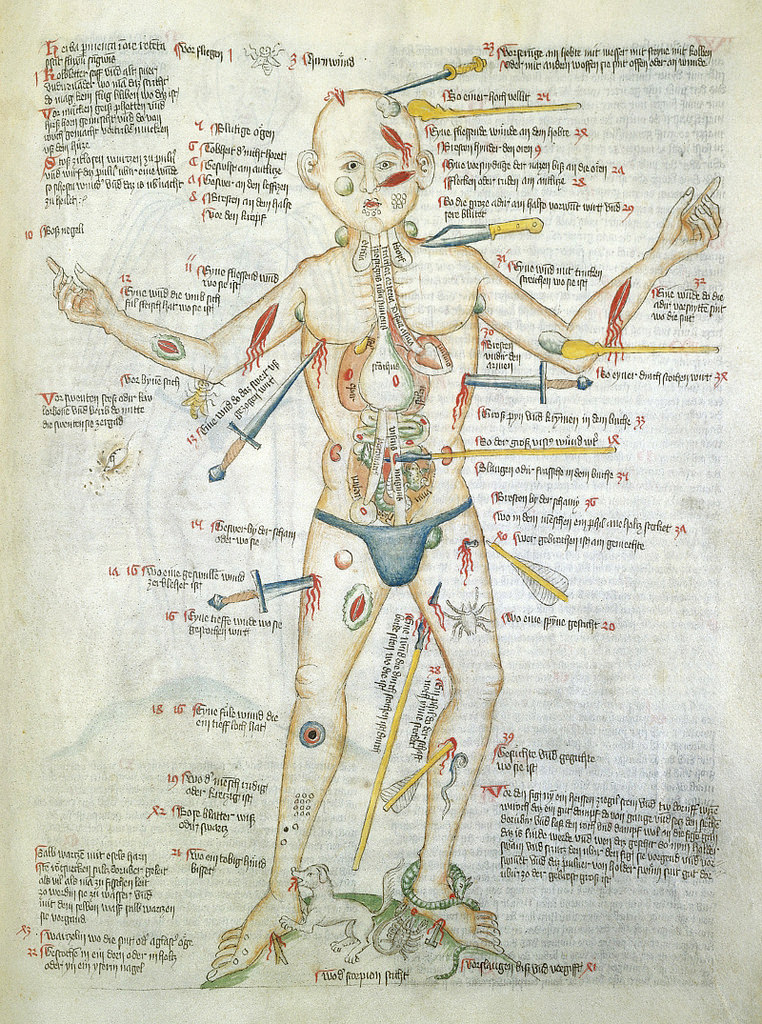
 Should we blame the creative originators of fake news, conspiracy theories, disinformation and click-bait hype? Or, should we blame the media for disseminating, spinning and aggrandizing these stories for their own profit or political motives? Or, should we blame us — the witless consumers.
Should we blame the creative originators of fake news, conspiracy theories, disinformation and click-bait hype? Or, should we blame the media for disseminating, spinning and aggrandizing these stories for their own profit or political motives? Or, should we blame us — the witless consumers.